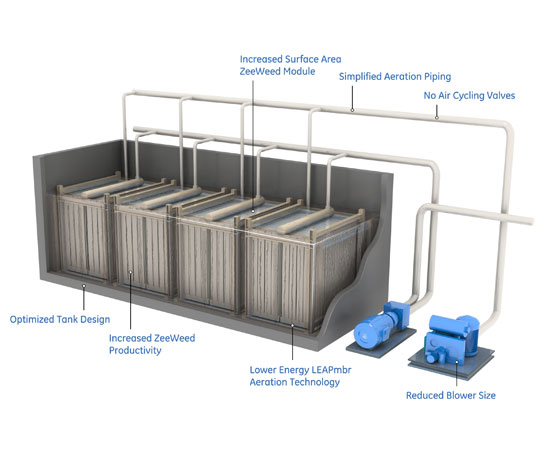
Description
Containerized Membrane BioReactor For Waste Water Treatment
Technical information
MBR technology can meet various wastewater treatment applications that require high-quality wastewater to meet regulatory requirements or can be reused. The membrane ensures high quality and one-stop responsibility. The targets of MBR are biological oxygen demand (BOD), total suspended solids (TSS), bacteria, total coliforms, ammonia, nitrogen and phosphorus.
MBR also eliminates many drugs from the waste stream, which is a growing concern for natural habitats and drinking water. With extensive experience in groundwater remediation, it can bring solutions to emerging pollutant challenges.
| Parameter | Feed Water Quality | Expected Permeate Quality |
| pH | 6.5-7.5 S.U. | 6.5-7.5 S.U. |
| Alkalinity (as CaCO3) | 125 mg/L | ≥100 mg/L |
| Temperature Range | 20-30°C | 20-30°C |
| TSS | 200 | <5 mg/L |
| Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) | 250 | < 10 mg/L |
| Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) | 400 | <50 mg/L |
| Ammonium-Nitrogen (NH4) | 30 | <2 mg/L |
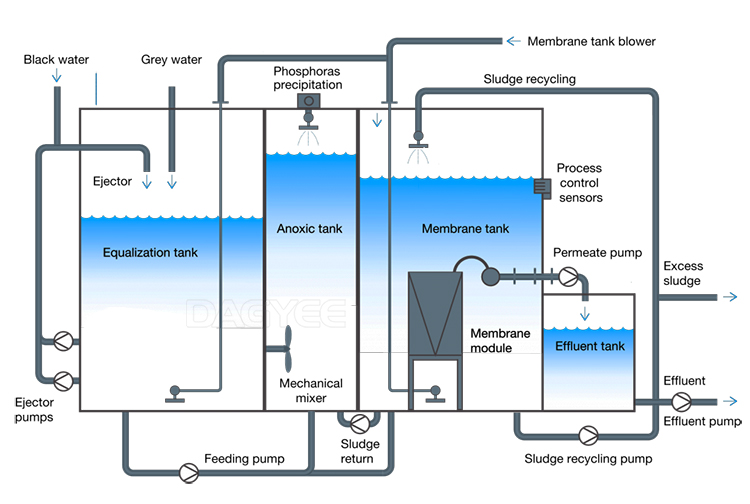
Information required for design
- Site conditions
- Hydraulic load conditions
- Wastewater characteristics
- Wastewater quality index
- Process design plan
- Components required for MBR process
- MBR process configuration
- Choose the course of treatment
- Based on total annual flow
- Used to design bioreactors, sludge treatment systems and define plant capacity
- Peak conditions
- Need flow and duration of peak flow
- The important conditions are the hourly peak and daily peak traffic
- Used to design the pretreatment process and membrane filtration system
- seasonal changes
- Flow and load changes due to seasonal or industrial activities
- Design biological processes using average daily flow and organic load during peak seasons
-
Average daily traffic
Wastewater characteristics
- The lowest parameters of MBR process design
- BOD, COD-estimated organic load rate
- TSS, VSS-design pretreatment system
- Estimated inert suspended solids (ISS) for MLSS and SRT calculations
- Nitrogen and Phosphorus-Design a nutrient removal process
- Verify that nutrients are sufficient (especially industrial wastewater)
- Alkalinity-designed for nitrification/denitrification and chemical phosphorus removal
- Temperature-minimum value for biological and membrane process design
Parameter
- Need to evaluate pretreatment options and special precautions
- Fat
- Heavy metal
- Toxins/foam inhibitors/antibiotics, etc.
- pH value
Applications
- Greenfield & Retrofit Projects
- Existing Infrastructure Tie-ins
- Municipal WWTPs
- Temporary or Interim Sewage Facilities
- New Residential Developments
- Hotels, Resorts & Restaurants
- Off-Grid & Remote Municipal Plants
- New Commercial Developments
Typical MBR wastewater quality
- According to municipal sewage
- BOD <5 mg/L (usually not detectable)
- TSS <5 mg/L (usually not detectable)
- NH3-N <1 mg/L (usually <0.5 mg/L)
- TN <10 mg/L (<3 mg/L can be achieved in warm climates)
- TP <0.5 mg/L (achievable <0.1 mg/L)
- Turbidity <1 NTU (95% of the time <0.2 NTU)
Discharge target (typical basic design)
- Discharge target (typical basic design)
- Biological oxygen demand (BOD) <5.0 mg / L
- Total suspended solids (TSS) <5.0 mg / L
- Ammonia nitrogen <1.0 mg/L
- Turbidity<0.5 NTU
- Total phosphorus <0.1 mg/L
- Total nitrogen <5.0 mg/L
- Enhanced nutrient removal design can achieve lower wastewater treatment effect:
- Total phosphorus <0.05 mg/L
- Total nitrogen <3.0 mg/L